Figure 1. Ectopic lymphoid tissue develops in the lungs of mice after viral infection.
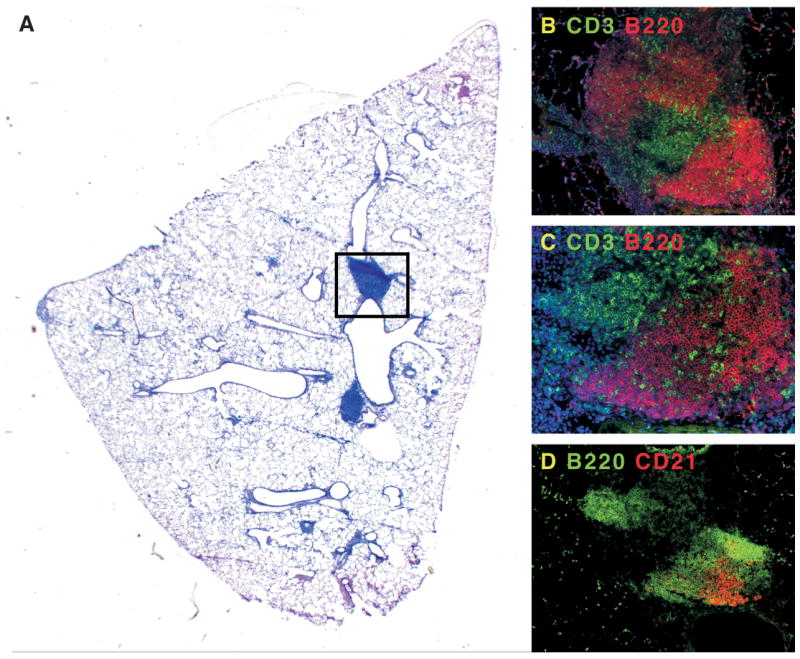
Mice were infected with murine γ-herpesvirus-68 and allowed to clear the lytic phase of the infection. A. Although the majority of the inflammatory response in the lung has resolved, areas of pulmonary lymphoid tissue remain next to major airways. B. The boxed area in panel A contains B220+ B cell areas (red), and CD3+ T cell areas (green). C. A magnification of the B cell areas shows infiltrating T cells. D. In a serial section of panel B, it is clear that some of the B cell follicles in iBALT (green) have CD21+ FDCs (red).
