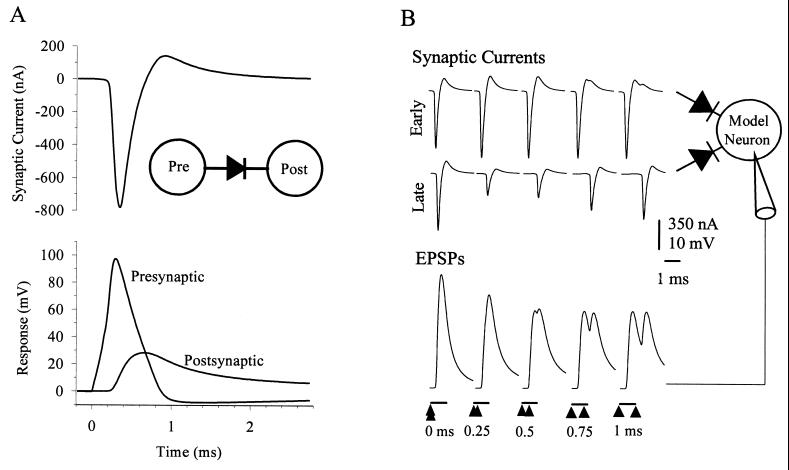
Figure 1.
Rectifying electrical synapses and coincidence detection in a model neuron. (A) Responses of a model rectifying electrical synapse. An action potential (Lower, Presynaptic) in a model presynaptic neuron (Inset, Pre ball) drives current (Upper) through the rectifying electrical synapse (Inset, black diode symbol), which produces an EPSP (Lower, Postsynaptic) in the model postsynaptic cell (Inset, Post ball). Note the delay in the onset of the EPSP and the reversal in synaptic current direction as the voltage across the synapse reverses. (B) Synaptic currents and EPSPs of a model neuron (circle in Inset) to coincident and asynchronous inputs through rectifying electrical synapses (diode symbols). The early synaptic currents (top traces at left) were evoked by presynaptic spikes identical to that in A through the top synapse (top diode symbol of Inset); the late synaptic currents (middle traces) were evoked by similar spikes presynaptic to the bottom synapse and delayed by the times given below the EPSPs. The EPSPs evoked by the early and late synaptic currents are at the bottom. The model was identical to that in A, except for the addition of a second synaptic input identical to the first.