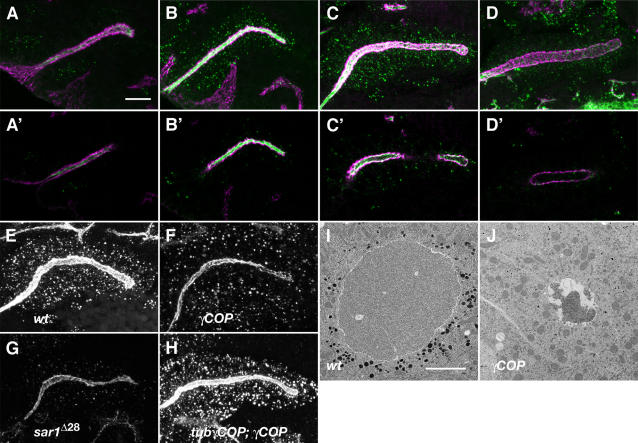
Figure 3. γCOP is required for deposition of O-glycans and luminal ECM assembly in the SG.
(A–H) Confocal projections show developmental stages of salivary gland (A–D) stained for Tn-antigen (green) and Crumbs in (magenta). (A′–D′) represent confocal sections of the (A–D) projections focused inside the lumen. (A, A′) show stage 11, (B, B′) stage 12, (C, C′) stage 13, (D, D′) stage 15 wild-type embryos. The salivary gland epithelium dynamically deposits Tn antigen into the lumen. While at stage 11 luminal levels of Tn antigen are low, they increase dramatically during stages 12 and 13 and localise to intracellular puncta and lumen. Later, luminal Tn antigen levels decline but a minor proportion remains along the apical epithelial membrane. (E–H) Confocal projections show stage 13 wild-type (E), γCOP/γCOP P1 (F), sar1 ΔEP28 (G) and tub-γCOP; γCOP/γCOP P1 mutant embryos (H) stained for Tn antigen (white). γCOP and sar1 mutant embryos show reduced intracellular puncta and luminal deposition of Tn antigen. (I and J) TEM of salivary gland cross-sections from stage 16 wild-type and γCOP mutants. The intraluminal matrix and the electron-dense granules are severely reduced in γCOP mutants compared to wild type. Scale bars are 10 µm in A–H. and 2 µm in I and J.