Fig. 1.
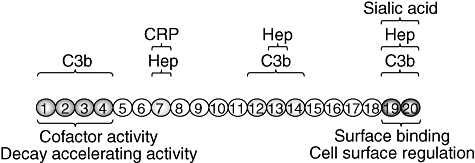
Functional domains in complement factor H. Factor H has three C3b-binding sites, short consensus repeats (SCR)1–4, SCR12–14 and SCR19–20, respectively [9–13]. Similarly, a total of three separate binding sites for heparin and sialic acid have been identified in SCR7, SCR13 and SCR19–20, respectively [14–17]. The critical sites for co-factor activity/decay accelerating activity and cell surface regulation at the N- and C-termini, respectively, are indicated. In addition to C3b and polyanion binding sites, there are other domains in factor H that have been shown to interact with plasma proteins or with micoorganisms and that are interesting because of their potential relevance in pathology. In this regard, it has been shown that factor H binds to C-reactive protein (CRP) which may help to counteract and inhibit the CRP-dependent alternative pathway activation induced by damaged tissue [18,19]. The heparin- and CRP-binding sites in SCR7 are overlapping sites in which one substrate inhibits the binding of the others [20].
