Fig. 2.
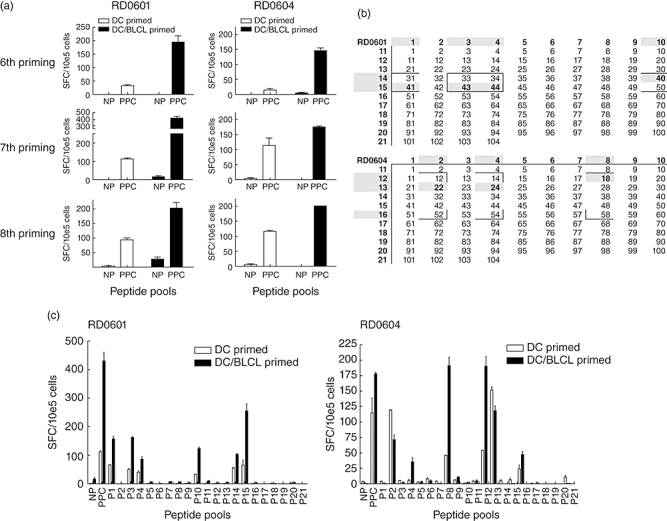
Peptide specificity and frequency of peptide reactive cells in dendritic cells (DC)-primed versus DC/B lymphoblastoid cell lines (BLCL)-primed lines. The frequency of interferon (IFN)-γ producing T cells responding to the complete pool of Aspergillus (Asp) f16 peptides [complete peptide pool pulsed pentadecapeptides (PPC)] was tested by enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) 1 week following the sixth, seventh and eighth primings for DC-primed lines and for DC followed by BLCL-primed lines (DC/BLCL) from donors RD0601 and RD0604. The results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) number of spot-forming cells (SFC) per 105 cells in replicate wells tested after addition of PPC-pulsed DC or non-pulsed (NP) DC (a). DC-primed and DC/BLCL-primed lines from both donors were tested after the seventh or eighth priming by IFN-γ ELISPOT for reactivity to 21 small pools of Asp f16 peptides. Results are expressed as mean ± s.d. of SPC per 105 cells plated in replicate wells (b). Based on the results of the small pool screening, candidate single peptides (boxed areas within the matrix) as well as the immediately flanking peptides were pulsed onto autologous DC and the DC-primed and DC/BLCL-primed lines were tested after the seventh or eighth priming by IFN-γ ELISPOT. Shaded areas indicate IFN-γ production significantly above background for the small pools (outer numbers) and for the single peptides (inner numbers) recognized by the T cell lines. For technical reasons candidate peptides 52, 54 and 58 for donor RD0604 were not tested. Similar to the small pool screening shown (b), the number of SPC/105 were higher in DC/BLCL-primed lines although the pattern of SP recognition was identical (c).
