Figure 8.
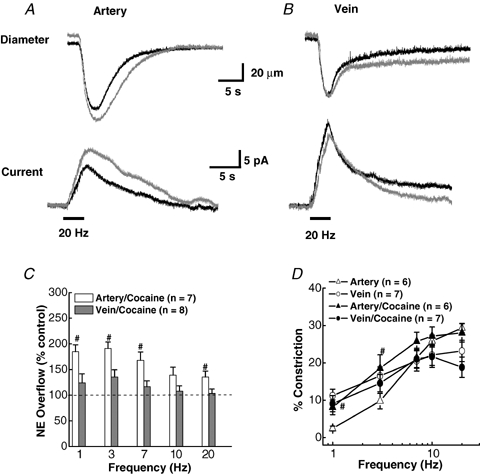
Effect of cocaine on NA oxidation current and neurogenic constriction in of MA and MV A, representative recordings of constriction (upper traces) and oxidation currents (lower traces) in a MA in the absence and presence of cocaine (10 μm). Cocaine increased the current but had little effect on the constriction. B, similar recordings in a MV. Cocaine did not change the NA oxidation current or constriction in MV. The bars under the current traces in A and B indicate the period of nerve stimulation (60 pulses with a 0.3 ms pulse width). C, frequency-dependent increase in the NA oxidation current in MA but not MV by cocaine. Data are of expressed as a percentage of the response obtained before cocaine treatment in each tissue. #Significantly different from control levels. D, frequency–response curves (1.0–20 Hz) for vasoconstriction in MA and MV in the absence (control) and in the presence of cocaine. #Significantly different from control levels for both MA (P < 0.05). Cocaine did not change constriction in MV at any stimulation frequency. Data are means ±s.e.m.
