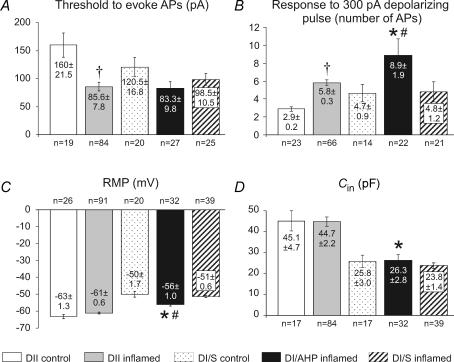
Figure 5. Comparisons of electrophysiological properties of Dogiel type II (DII) and Dogiel type I (DI) neurons from the control and inflamed ileum.
Five groups are compared: DII neurons from control and inflamed ileum, DI neurons from control, DI neurons that exhibited late AHPs from the inflamed ileum and DI neurons that did not exhibit late AHPs from the inflamed ileum. A, thresholds for action potential generation in DII neurons from the inflamed ileum were significantly lower than from control (P < 0.001). Differences between DI neurons were not significant. B, excitability, measured as the numbers of action potentials elicited by 500 ms depolarizing pulses, was significantly greater for DI/AHP neurons from the inflamed intestine compared with DI neurons from control or DI/S neurons from the inflamed ileum (P < 0.05). Excitability was also increased for DII neurons from the inflamed ileum compared with DII neurons from the control ileum (P < 0.05). C, the resting membrane potential (RMP) was not changed in DII neurons, although DI/AHP neurons from the inflamed ileum were more hyperpolarized than DI/S inflamed or control DI neurons (P < 0.05), but less hyperpolarized than DII neurons from the inflamed ileum (P < 0.001). D, there were no significant differences in neuron capacitance. DI/AHP neurons from the inflamed intestine were significantly smaller than DII neurons. Values of mean ± s.e.m. and numbers of neurons analysed for each parameter are incorporated into the histograms. *Significantly different from Dogiel type II neurons from the inflamed ileum (P < 0.05). #Significantly different from Dogiel type I/S neurons from the inflamed ileum (P < 0.05). †Significantly different from Dogiel type II neurons from the control ileum (P < 0.05).