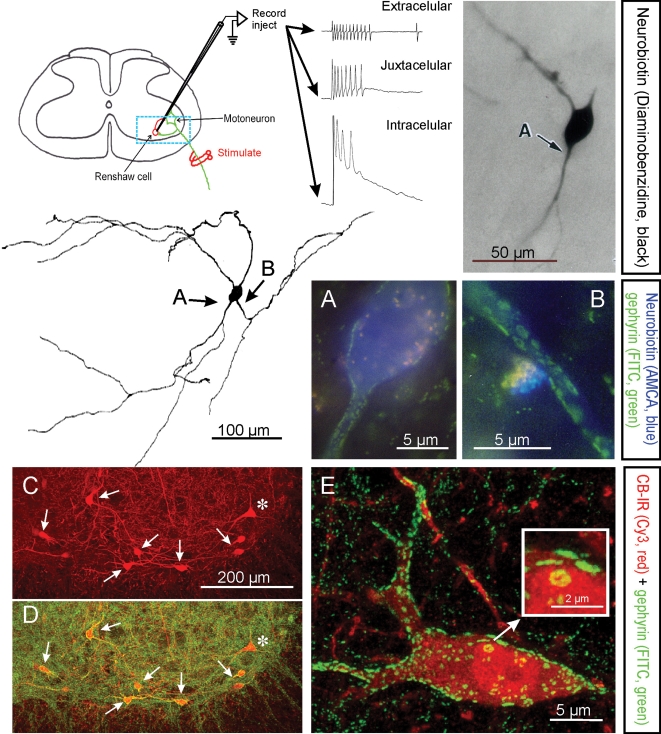
Figure 1. Electrophysiological, morphological and neurochemical characteristics of Renshaw cells.
Renshaw cells are classically identified by their high-frequency discharge in response to antidromic motor axon action potentials recorded either extracellulary, juxtacellularly or intracellularly. The diagram shows the basic experimental set-up and resulting recordings. The typical high-frequency burst of action potentials recorded extracellularly is diminished following impalement of the cell but a long EPSP is revealed. The blue box indicates the approximate region of neuropil represented in C and D. Electrophysiologically identified Renshaw cells were injected with neurobiotin (Alvarez et al. 1997), which was initially revealed with α-methyl-coumarin (AMCA) to allow visualization of the pattern of gephyrin immunolabelling (FITC fluorochrome) on the recorded cell. Subsequent processing with diaminobenzidine permitted full reconstruction of the dendritic trees of the same cells. In this manner it was found that Renshaw cells are characterized by very large patches of gephyrin immunoreactivity in their proximal dendritic regions and somatic membrane; the frequency of these clusters drops markedly on more distal dendrites (Alvarez et al. 1997). A and B show at high magnification gephyrin-immunoreactive clusters in the regions indicated with arrows in the reconstructed neuron. C and D, Renshaw cells are also strongly immunoreactive (IR) for calbindin and the large majority of calbindin-IR cells in the ventral spinal cord display the large gephyrin clusters characteristic of Renshaw cells. In the confocal images shown in C and D only one calbindin-IR cell (*) did not display large gephyrin-IR clusters and was probably not a Renshaw cell. Non-Renshaw calbindin-IR cells tend to have larger cell bodies and do not receive strong inputs from cholinergic boutons. E, 2D projection of a 3D reconstructed calbindin-IR Renshaw cell displaying the characteristic large gephyrin clusters (note much larger clusters on the calbindin-IR cells than in the adjacent neuropil). One large cluster in the soma is shown magnified in the inset. Gephyrin-IR clusters represent inhibitory postsynaptic densities and the ones on Renshaw cells are among the larger found in the spinal cord.