Table 2.
Cerebrovascular resistance during hypoxia and hypercapnia with pharmacological interventions
| Hypoxia | Hypercapnia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Lead-in | 5 min | 20 min | Recovery | Lead-in | 5 min | 20 min | Recovery |
| Control | 1.44 ± 0.34 | 1.40 ± 0.32 | 1.42 ± 0.32 | 1.52 ± 0.31 | 1.39 ± 0.32 | 1.14 ± 0.25* | 1.20 ± 0.26* | 1.63 ± 0.30* |
| l-NMMA | 1.51 ± 0.44 | 1.44 ± 0.43* | 1.42 ± 0.41* | 1.51 ± 0.46 | 1.56 ± 0.51 | 1.29 ± 0.41* | 1.32 ± 0.38* | 1.75 ± 0.50* |
| Phenylephrine | 1.50 ± 0.40 | 1.50 ± 0.37 | 1.48 ± 0.36 | 1.55 ± 0.35 | 1.47 ± 0.29 | 1.24 ± 0.22* | 1.26 ± 0.23* | 1.73 ± 0.25* |
Values (Torr (cm s−1)−1) are means ±s.d. Cerebrovascular resistance was calculated as MAP divided by 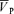 .
. 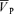 , middle cerebral artery blood velocity associated with the maximum frequency of the Doppler shift; MAP, mean arterial blood pressure.
, middle cerebral artery blood velocity associated with the maximum frequency of the Doppler shift; MAP, mean arterial blood pressure.
denotes a significant difference from lead-in at P < 0.05.
