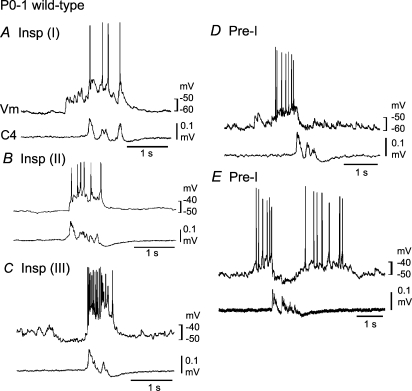
Figure 1. Respiratory neurons in the ventrolateral medulla of neonatal wild-type mice.
Neurons were recorded in the ventrolateral medulla of the brainstem–spinal cord preparation (without pons) from postnatal day 0–1 wild-type mice in the presence of 0.1–0.2 μm adrenaline (see supplemental Fig. 1 for activity in the absence of adrenaline). A, a type I inspiratory (Insp) neuron receiving excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) prior to onset of inspiratory nerve discharge. B, a type II Insp neuron in which EPSPs occur only during the inspiratory phase. C, a type III Insp neuron hyperpolarized by synchronized inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) during the preinspiratory phase. D, a type I preinspiratory (Pre-I) neuron showing action potential discharges predominantly during the preinspiratory phase. E, a type II Pre-I showing action potential discharges during pre- and postinspiratory phases. Vm, membrane potential trajectory; C4, C4 inspiratory activity.