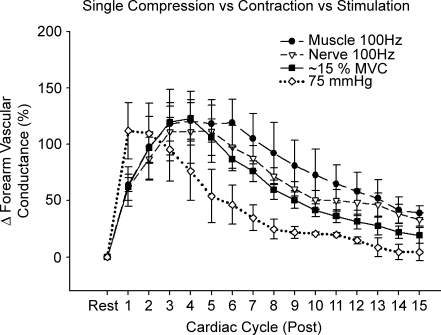
Figure 6.
Effects of muscle and nerve stimulation on forearm vasodilator responses and the temporal association with mechanically and voluntary contraction-induced rapid vasodilatation Electrical stimulation of both the forearm muscle belly and median nerve evoked a significant vasodilatation (P < 0.05). Of importance, when these responses were compared with those following voluntary contractions, the temporal pattern was similar. By contrast, the temporal pattern of the mechanically induced vasodilatation was dissociated from all muscle contraction conditions (n = 4.) Peak vasodilator responses for both forearm compressions and voluntary contractions were matched to those observed in response to electrical stimulation. Maximum voluntary contraction, 10% for three subjects and 25% for one subject.