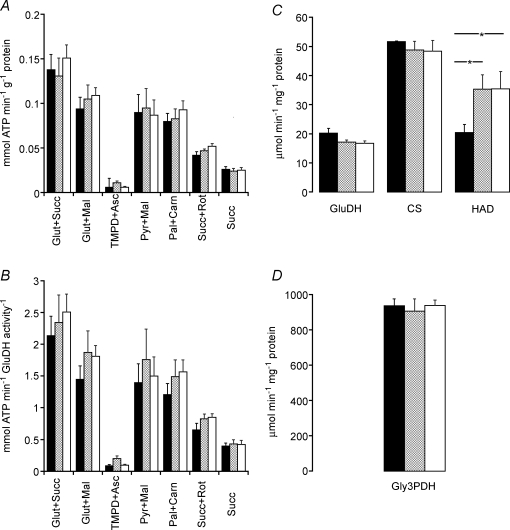
Figure 1.
Maximal rates of ATP production in skeletal muscle A and B, maximal rate of mitochondrial ATP production at 25°C, using a variety of substrates, normalized to either mitochondrial protein content (A) or to mitochondrial density (activity of glutamate dehydrogenase; B) measured in soleus muscle of rats fed with either vehicle (hydroxypropylmethylcellulose) (filled columns) or GW610742 at 5 mg (kg bm)−1 (cross-hatched columns) and 100 mg (kg bm)−1 (open columns). C and D, enzymatic activities of glutamate dehydrogenase (GluDH), citrate synthase (CS), β-hydroxyl acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase (HAD) (C) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gly3PDH, D) normalized to the protein content measured in soleus muscle of rats fed with either vehicle (hydroxypropylmethylcellulose) (filled columns) or GW610742 at 5 mg (kg bm)−1 (cross-hatched columns) and 100 mg (kg bm)−1 (open columns). *Significantly different from the corresponding control (vehicle) group (P < 0.05).