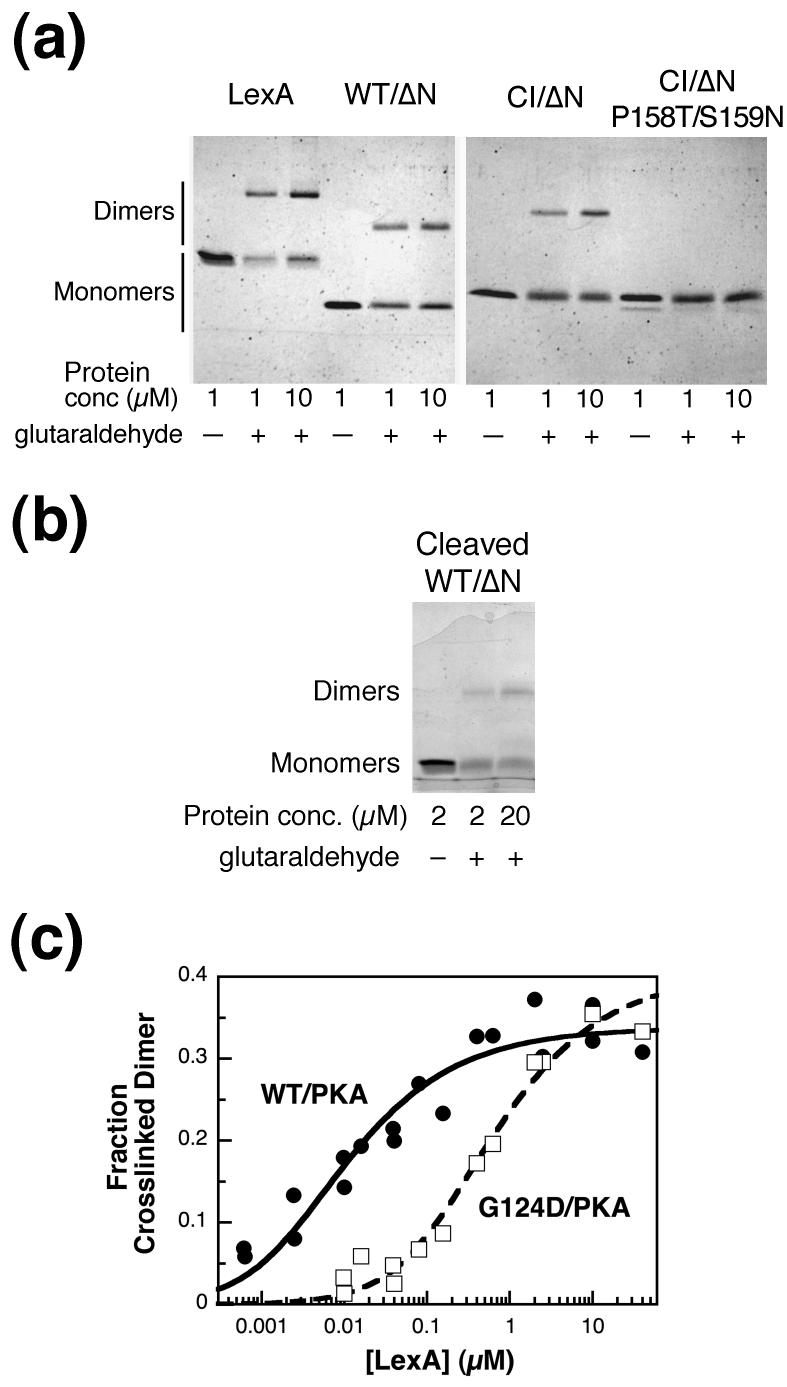
Figure 4.
Cross-linking of LexA and truncations. (a) LexA, WT/ΔN, CI/ΔN, and CI/ΔN P158T/S159N at 1 and 10 μM were incubated at 30°C in the presence or absence of 8 mM glutaraldehyde for 10 min, as indicated. Equal molar amounts of each sample were run on 15% Laemmli gels and stained with Coomassie blue. The faint band under CI/ΔN P158T/S159N is cleaved protein, presumably resulting from autodigestion, that was present after the protein purification. (b) An experiment done as in part (a) was carried out with cleaved LexA WT/ΔN at 2 or 20 μM. A higher concentration was used than in part (a) because the C-terminal fragment, like full-length LexA, did not resolve well after cross-linking at lower concentrations. (c) Radiolabeled WT/PKA (closed circles) and G124D/PKA (open squares) were cross-linked as above at the concentrations indicated, and the amount of protein in the dimer band was quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Each data point represents one sample, and the data from multiple experiments have been combined. Data were fit to curves for a monomer-dimer equilibrium to calculate the KD and the maximum cross-linked dimer (max), where L is the concentration of the LexA truncation. Fraction Cross-linked Dimer Observed=(max)*(4L+ KD- (KD2+ 8L* KD)1/2)/4L, where L is the concentration of the LexA truncation. KD= 10 ± 3 nM, max= 0.34 ± 0.01 for WT/PKA and KD= 0.6 ± 0.1 μM, max= 0.40 ± 0.02 for G124D/PKA.