Fig. 2. S426A/S430A CB1 receptor internalization and pharmacological blockade of CB1 receptor internalization with Concanavalin A.
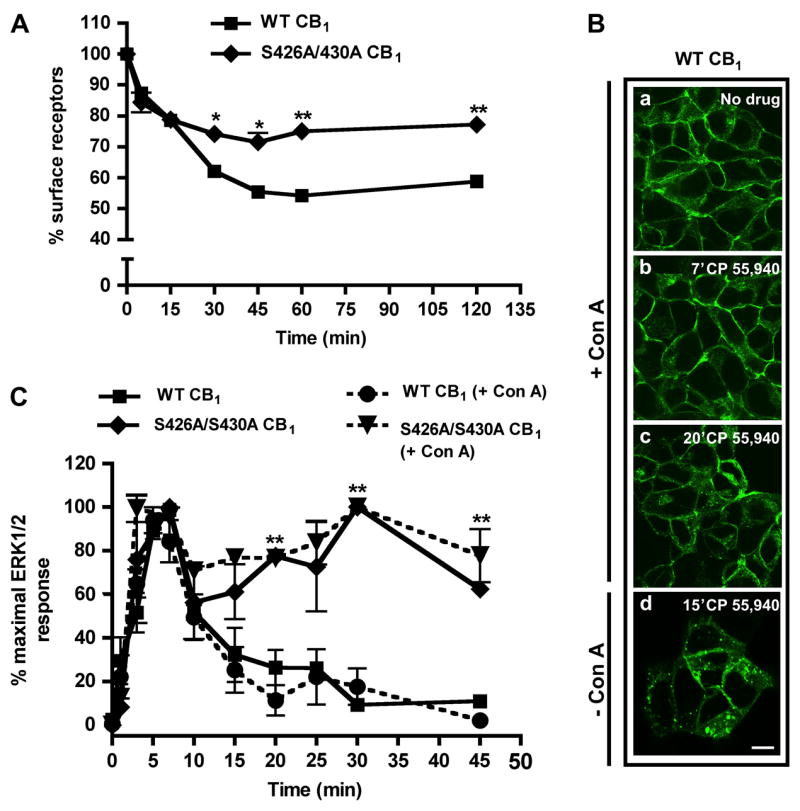
(A) Agonist-induced internalization of wild-type and S426A/S430A CB1. Cells were treated with 100 nM CP 55,940 for the indicated times at 37°C. Loss of cell surface receptors was quantified as described in Methods. Rapid (≤ 15 min) receptor endocytosis was unaffected by the S426A/S430A mutation. However, the extent of S426A/S430A CB1 receptor internalization was significantly attenuated following prolonged drug treatment (≥ 30 min). Data are mean ± SEM; n = 15–20 from three to five experiments performed in quadruplicate. **p<0.01 and *p<0.05 compared with wild-type CB1 receptor internalization by unpaired t-test. (B) Immunostaining of wild-type CB1 receptors following Con A treatment. Cells were pretreated with HBS containing 100 μg/ml Con A (a–c) or HBS alone (d) for 30 min, followed by stimulation with 100 nM CP 55,940 for the indicated times. Con A prevented significant CB1 receptor internalization at both time points evaluated. In the absence of Con A, a significant fraction of CB1 receptors were internalized after 15 min (d). Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Time course of ERK1/2 activation in the presence or absence of Con A. Cells were pretreated with either HBS alone or 100 μg/ml Con A for 30 min (+Con A groups). Following pretreatment, the cells were stimulated with 10 nM CP 55,940 alone or in the presence of Con A (+Con A groups). Inhibition of CB1 receptor internalization by Con A (wild-type or S426A/S430A) does not affect the kinetics of ERK1/2 activation. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 5–15 from two to three experiments performed in duplicate. **p<0.01 compared with wild-type CB1, no Con A by unpaired t-test.
