Fig. 2.
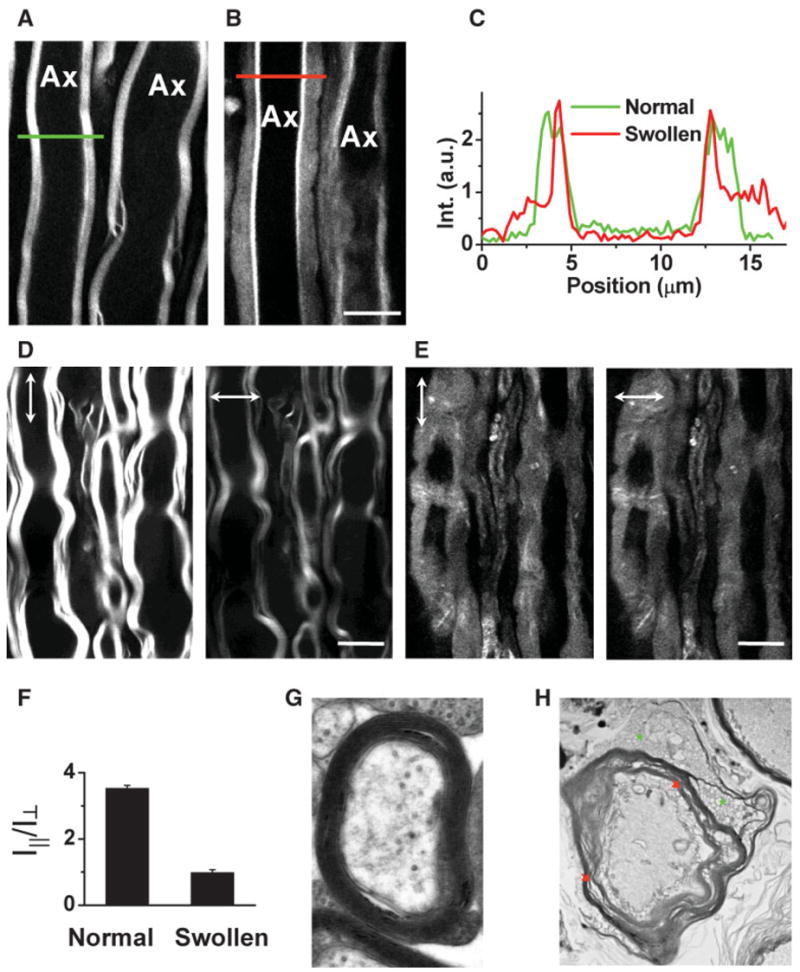
Characterization of lyso-PtdCho-induced myelin swelling by CARS microscopy and EM. The laser beams were focused into the equatorial plane of axons. A: CARS image of normal myelin sheath wrapping two parallel axons acquired at a speed of 1.13 sec/frame. The same speed was used for other images. B: CARS image of partially swollen myelin sheath acquired at 5 min after injecting 2 μl of 10 mg/ml lyso-PtdCho into the tissue. C: CARS intensity profiles of normal and swollen myelin fibers. Green: taken along the green line in A. Red: taken along the red line in B. Note the decrease of CARS intensity in the swollen region. D: CARS images of normal myelin sheath with vertical (vertical arrows) and horizontal (horizontal arrows) excitation polarization. E: CARS images of totally swollen myelin sheath with vertical (vertical arrows) and horizontal (horizontal arrows) excitation polarization. F: The ordering degree characterized by I||/I⊥ of intramyelin lipids for normal and swollen myelin sheath. The CARS intensity from the swollen myelin showed no dependence on the excitation polarization. G,H: TEM images of normal myelin (G, × 30,000) and degraded myelin induced by incubating the spinal tissue with 10 mg/ml lyso-PtdCho for 90 min (H, × 6,300). In H, green stars indicate myelin vesiculation and red arrows indicate myelin splitting. Scale bars = 10 μm. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
