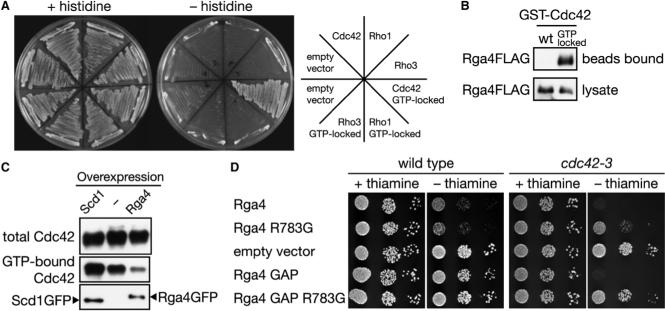
Figure 3. Rga4 Is a GAP for Cdc42.
(A) Rga4 interacts specifically with the GTP-bound form of Cdc42. Interaction of the Rga4 RhoGAP domain with the wild-type and GTP-locked mutants of Cdc42, Rho1, and Rho3 was assessed by histidine auxotrophy in the yeast two-hybrid assay. (B) Rga4 binds to the GTP-locked mutant of Cdc42. Bacterially expressed wild-type and GTP-locked mutant of GST-Cdc42 was immobilized to glutathione-beads and incubated with cell lysate of a rga4:FLAG strain, followed by anti-FLAG immunoblotting. (C) Overexpression of Rga4 reduces the cellular level of GTP-bound Cdc42. GFP-tagged Scd1 and Rga4 proteins were expressed from the nmt1 promoter in a strain carrying the HA:cdc42 allele. GTP-bound HA-Cdc42 in the cell lysate was collected by CRIB-beads, and detected by anti-HA immunoblotting. Overexpression of the GFP-tagged proteins was monitored by anti-GFP immunoblotting. (D) Overexpression of Rga4 or its GAP domain inhibits growth of the cdc42−3 mutant. Wild-type and cdc42−3 strains were transformed with the pREP1 vector (“empty vector”) and pREP1 carrying full-length rga4+, rga4R783G or their truncated fragments encoding the GAP domain (residues 681−933). Serial dilutions of the transformants were spotted onto EMM agar medium with or without thiamine and incubated at 30°C.