Figure 1. Two classical GCGR-mediated intracellular signalling pathways in glucagon-targeted cells.
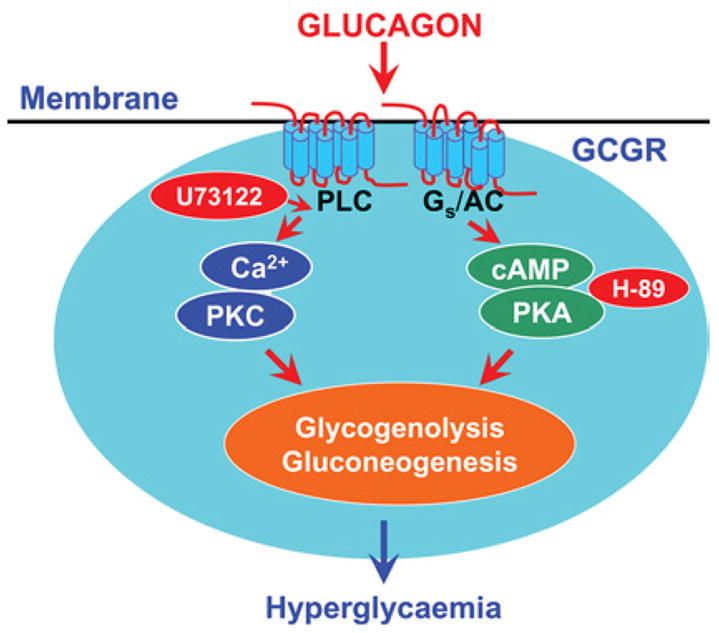
To induce an effect, glucagon binds to cell-surface Gs-protein-coupled receptors and activates the PLC/IP3/Ca2+ and PKA signalling pathways. Both signaling pathways are closely involved in mediating glucagon-induced glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, leading to hyperglycaemia. Pharmacological agents known to block these two signalling pathways (H-89, a selective PKA inhibitor, and U-73122, a selective PLC inhibitor) also inhibit glucagon-induced hyperglycaemic and growth effects in target cells. AC, adenylate cyclase; PKC, protein kinase C.
