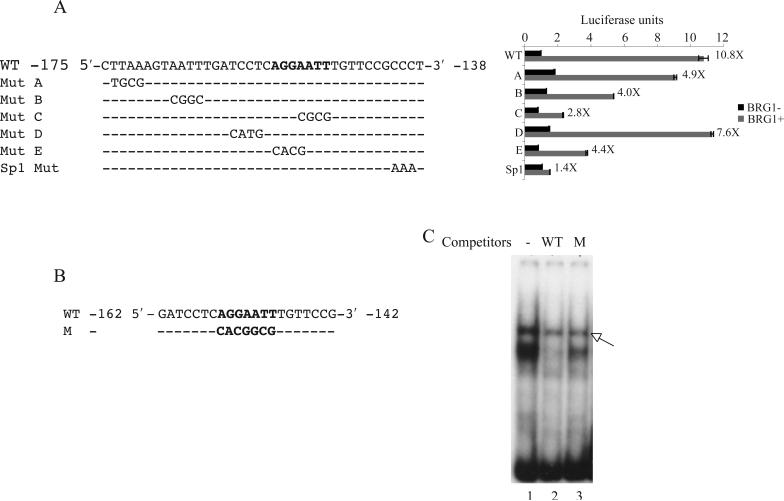
Fig.1.
Identification of the sites critical for the BAF complex dependent regulation of IFITM3 promoter. (A) Left panel: Sequence between the positions −175 and −138 of the IFITM3 promoter in the luciferase reporter constructs (pREP4-TM3-Luc). WT:wild type promoter. The 7-bp site important for the IFITM3 promoter activation is shown in bold. Mut A to Mut E : promoter mutants, mutated sites are indicated; Sp1 Mut: Sp1 binding site mutant. Right panel: luciferase activities of the corresponding constructs. (B) Sequence of the oligonucleotide probes used for EMSA in Figures 1C and 3A, B and C. WT: wild-type probe; M: mutant probe, mutated site shown in bold. (C) EMSA with SW-13 nuclear extracts. A 100-fold excess of the wild-type or mutant competitors were used. WT: wild-type competitor (Lane 2), M: mutant competitor (Lane 3), Lane 1: no competitor. Arrow - non-specific band