FIGURE 5. Sema4D−/− GVL effects.
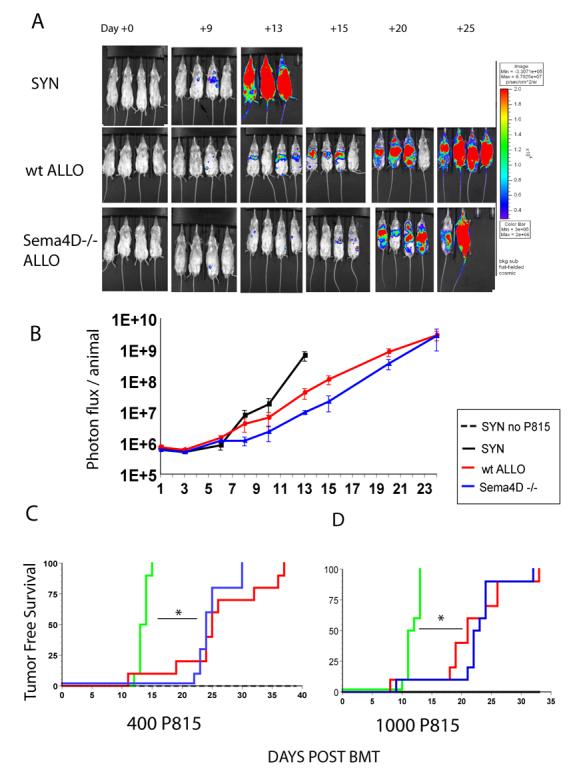
BALB/c (syngeneic H2d), B6 wt (allogeneic H2b) or Sema4D−/− (allogeneic H2b) recipients were irradiated with 800cGy and intravenously given 5.0×106 BM cells from BALB/c (syngeneic) or wt B6 (allogeneic groups) mice, plus either 5.0×105 wt B6 (allogeneic control), Sema4D−/− T cells (experimental) or BALB/c T cells (syngeneic control). 400 P815 tumor cells were added into the BM inoculum of all groups. A syngeneic [BALB/c→BALB/c] control group did not receive tumor.
A) BLI images show progression of tumor growth systemically over 24 days n=4/group. Tumor burden in Sema4D−/− T cell recipients is similar to B6 wt T cell recipients. (B) Mean values ± SEM for photon flux/animal (n = 4 mice). (C and D) Tumor free survival n=6 syngeneic without tumor, n=10 syngeneic + P815, n=10 allo B6 wt T cell recipients + P815 and n=10 allo Sema4D−/− T cell recipients + 400 P815(C) or 1000 P815 (D). Improved tumor free survival in allogeneic T cell recipients compared to the syngeneic recipients in both tumor challenges. Sema4D−/− allogeneic T cell recipients had a similar GVL effect as wt T cell control allogeneic recipients. *p<0.01
