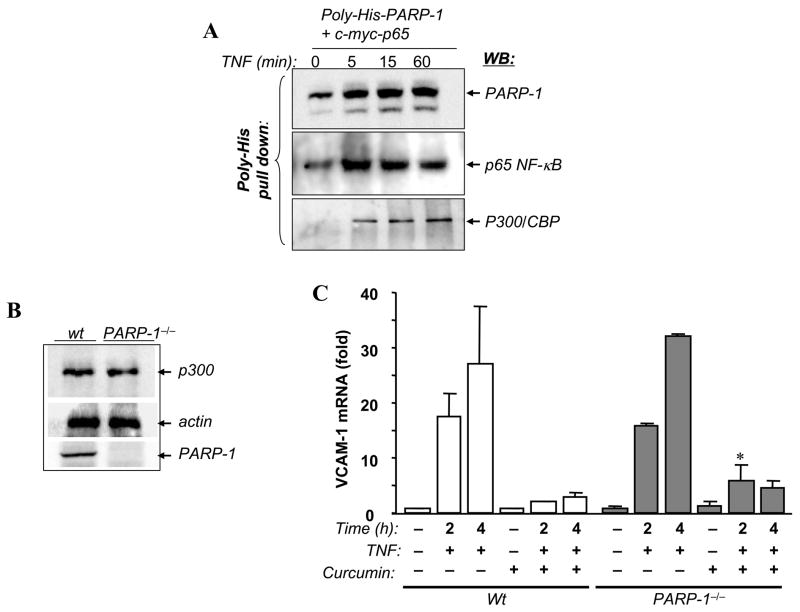
Fig. 4.
Transient interactions between PARP-1 and p300/CBP and the requirement of p300/CBP acetylation activity for VCAM-1 expression after TNF treatment. (A) A549 cells were co-transfected with expression vectors encoding PARP-1 tagged with poly-His and p65 NF-κB or with empty vectors. Cells were treated with TNF for the indicated time intervals after which total protein extracts were prepared and subjected to a nickel bead-based pull-down assay. Precipitates were then subjected to immunoblot analysis (WB) with antibodies to PARP-1, p65 NF-κB, or p300/CBP. (B) Protein extracts from Wt or PARP-1−/− SMCs were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to p300/CBP PARP-1 or actin. (C) Wt or PARP-1−/− SMCs were treated with TNF for the indicated time intervals in the presence or absence of 10 μM curcumin, a specific inhibitor of p300/CBP, after which total RNA was extracted and subjected to cDNA generation followed by real-time PCR analysis using primers specific to mouse VCAM-1 or β-actin. *, difference from the Wt counterpart, p < 0.05.