Figure 1.—
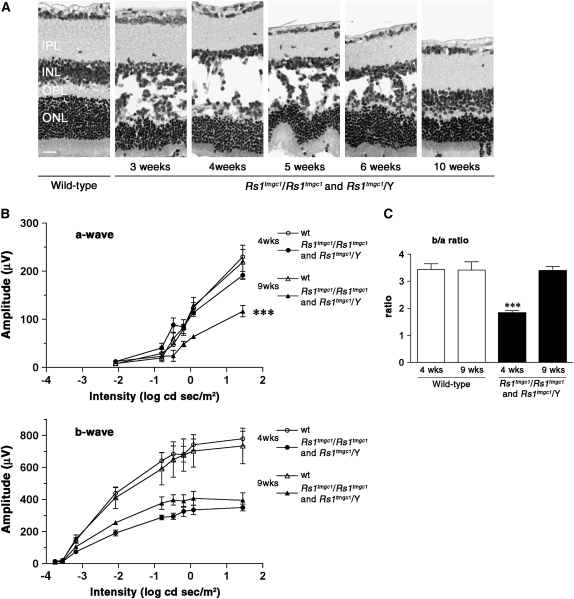
Schisis progression and ERG b-wave response in Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice. (A) Schisis is most severe at 4 weeks of age and decreases over time. Note that adult (10-week-old) Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice do not have schisis. Images of H&E stained paraffin sections are shown. (B) ERG a-wave (top) and b-wave (bottom) responses in Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice at 4 and 9 weeks of age. The graphs show the average response at increasing light intensities for wild-type and Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice. Nine-week-old Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice have a reduced a-wave and slightly higher b-wave amplitude than 4-week-old mice. (C) The b/a-wave ratio in wild-type and Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice at 4 and 9 weeks of age. Nine-week-old Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice have an improved b/a-wave ratio compared to 4-week-old Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice. IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; wt, wild type; bar, 20 μm; ***P < 0.0001.