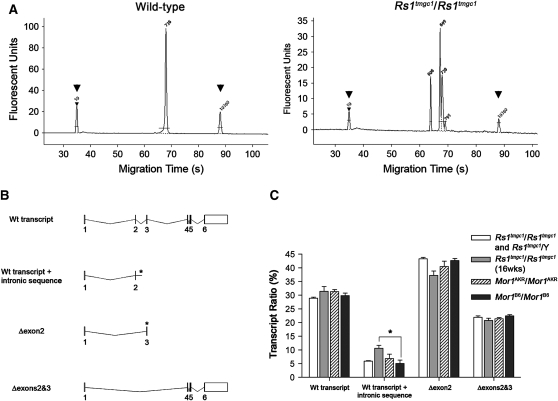
Figure 6.—
Population of transcripts in Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y and B6 congenic mice. (A) Representative electropherograms for Rs1 transcripts in the mouse retina. Wild-type mice show one major peak corresponding to the full-length wild-type transcript (738 bp), while male and female Rs1tmgc1 mutant mice show a full-length transcript plus three alternative transcripts at 609 bp, 699 bp, and 787 bp. Control peaks are labeled with arrowheads. (B) Splicing variants of Rs1. The diagram illustrates the mouse Rs1 wild-type transcript and the three splice variants found in Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y retinas. The asterisks denote the formation of premature stop codons. (C) Relative amount of transcript variants found in Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y retinas. The amount of each transcript variant is shown as a percentage of total transcripts in Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 and Rs1tmgc1/Y mice and B6 congenic (B6.Cg-Rs1tmgc1) mice that are Mor1AKR/Mor1AKR or Mor1B6/Mor1B6. Mice were tested at 4 weeks of age unless noted. The ratios for wild-type transcripts, transcripts that skip exon 2, and transcripts that skip both exons 2 and 3 are not significantly different among all groups tested. The ratio of wild-type transcripts with intronic sequence is significantly different (P < 0.05) between Mor1B6/Mor1B6 and 16-week-old Rs1tmgc1/Rs1tmgc1 mice.