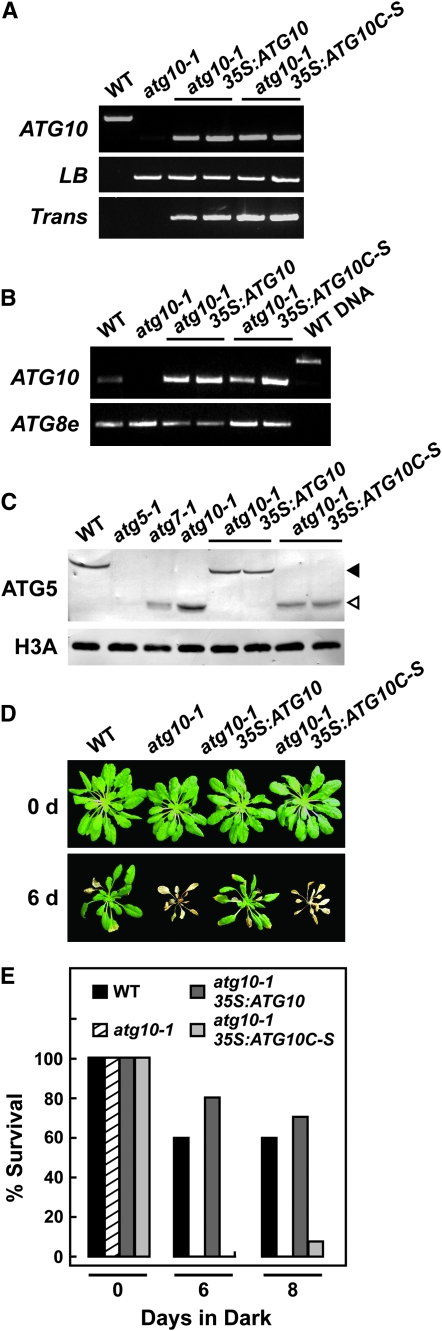
Figure 7.—
Attempted rescue of the atg10-1 phenotype with the 35S:ATG10 and 35S:ATG10C-S transgenes. (A) PCR analysis of the atg10-1 mutant and complemented plants. Total genomic DNA was subjected to PCR using either the ATG10 5′- and 3′-gene-specific primers (ATG10) or the T-DNA left border and ATG10 3′-primers (LB) or primers specific to the transgene (Trans). (B) Semiquantitative RT–PCR of the atg10-1 mutant and complemented plants. Total RNA was subjected to RT followed by 28 cycles of PCR using ATG10 5′- and 3′-gene-specific primers. A primer pair specific for ATG8e was used as an internal control. (C) Immunoblot detection of the ATG12-ATG5 conjugate in atg10-1 mutants complemented with 35S:ATG10 or the 35:ATG10C-S transgene. Tissue was collected from wild-type (WT), atg5-1, atg7-1, atg10-1, atg10-1/35S:ATG10, and atg10-1/35S:ATG10C-S seedlings and subjected to SDS–PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-ATG5 antibodies. Equal protein loads were confirmed by immunoblot analysis with anti-H3A antibodies. Open and solid arrowheads identify free ATG5 (40 kDa) and the ATG12-ATG5 conjugate (50 kDa), respectively. (D and E) Survival under C-limiting growth conditions induced by extended darkness. Six-week-old plants were grown under SD, exposed to 6 or 8 days of continuous darkness, and then transferred back to SD. (D) Representative plants after a 1-week recovery from darkness. (E) Percentage of plants that survived 6 or 8 days of continuous darkness as determined by resumption of growth after 1 week in SD. Each bar represents the analysis of 10 seedlings.