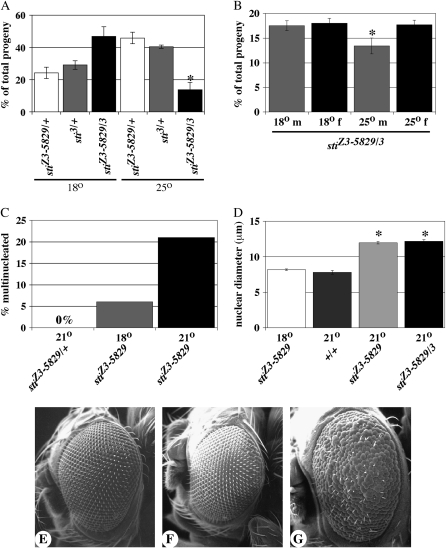
Figure 3.—
The stiZ3-5829 is a temperature-sensitive allele. (A) Graph compares the percentage of total progeny that result from the cross stiZ3-5829/TM6B × sti3/TM6B at 18° and 25°. Open bars, stiZ3-5829/TM6B. Shaded bars, sti3/TM6B. Solid bars, stiZ3-5829/sti3. No significant difference was observed between heterozygous progeny and stiZ3-5829/sti3 (P = 0.25, n = 338) at 18° whereas stiZ3-5829/sti3 progeny were significantly reduced at 25° (asterisk, P < 0.03, n = 398). (B) Both male (m) and female (f) stiZ3-5829/sti3 progeny are equally represented at 18° (P = 0.38, n = 3682) whereas male progeny are significantly reduced at 25° (asterisk, P = 0.01, n = 4193). (C) Multinucleated follicle cells are never observed in stiZ3-5829/+ ovaries (0%, n > 1000 egg chambers) while stiZ3-5829 homozygotes have ∼6% multinucleated cells at 18° (shaded bar, n = 200). stiZ3-5829 homozygotes have ∼22% multinucleated cells at 21° (solid bar, n = 200). (D) Nuclear diameters of sticky mutant follicle cells in stage 12–13 egg chambers at 18° (open bar) and wild type at 21° (+/+, darkly shaded bar) have normal size, ranging from 6 to 11 μm. The nuclear diameters of both stiZ3-5829 homozygotes (lightly shaded bar) and stiZ3-5829/sti3 (stiZ3-5829/3, solid bar) at 21° are significantly larger than stiZ3-5829 homozygotes at the permissive 18° (asterisks, P < 0.001, n = 200 for each genotype). (E and F) Scanning electron microscopy of the eyes of stiZ3-5829/+ (E), sti3/+ (F), and (G) stiZ3-5829/sti3 at 25°. Magnification, ×150.