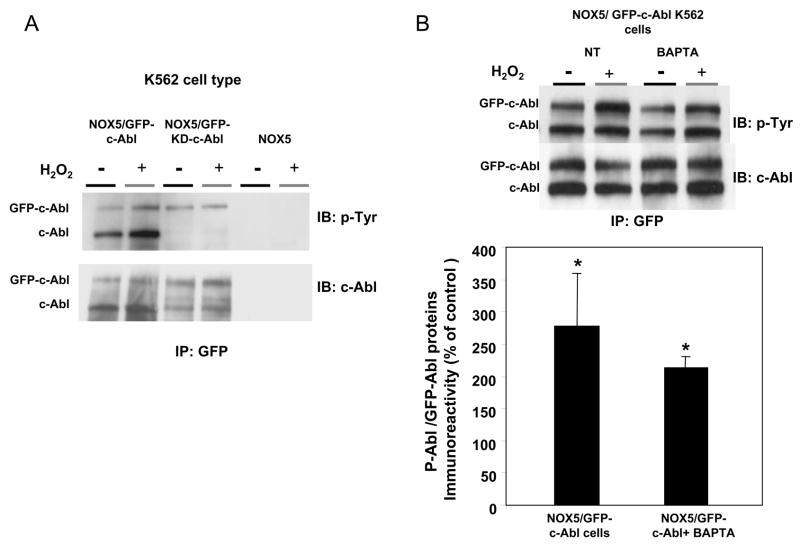
Fig. 7. Effect of H2O2 on c-Abl phosphorylation.
(A) Immunoprecipitation of GFP-tagged Abl was performed using anti-GFP antibodies and 250 μg of proteins obtained from lysates of K562/NOX5 cell expressing either kinase-active GFP-c-Abl or the kinase-dead GFP-c-Abl. The immunoprecipitated proteins were immunoblotted with phosphotyrosine or c-Abl antibody. K562/NOX5 cells were used as a negative control. (B) Immunoprecipitation experiment were performed as in A, except that the K562/NOX5 cells expressing wild-type GFP-c-Abl were either untreated or incubated with BAPTA (50 μM) and then treated (or not treated) with 100 μM H2O2 for 10 minutes. In the GFP immunoprecipitates, the levels of phosphorylated Abl proteins (GFP-c-Abl plus endogenous c-Abl) were calculated from their individual autoradiographic densities and normalized to the corresponding GFP-tagged protein level. All values obtained were then expressed as a percentage of the control value obtained from H2O2-untreated cells. Data are the mean +/− SEM of 3 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistical significance versus cells without H2O2. * P <0.05, **P <0.01.