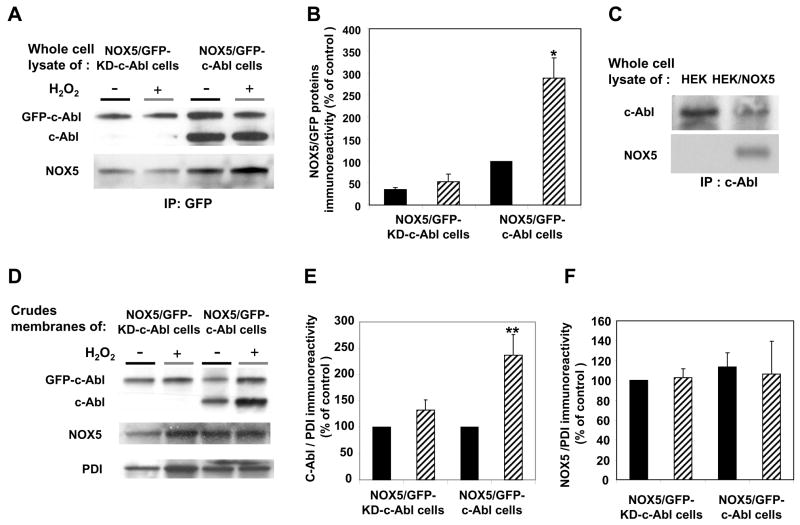
Fig. 8. Colocalization and functional interaction of wild type c-Abl with NOX5 activity in a cell-free assay.
(A) Lysates from K562/NOX5 expressing either kinase-active GFP-c-Abl or the kinase-dead GFP-c-Abl, and treated with or without 100μM H2O2, were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP as described in Fig. 7, and immunoblotted with antibodies to c-Abl and NOX5. (B) After densitometric analysis, the NOX5 protein content in the GFP-immunoprecipitates was determined and normalized to the corresponding GFP protein level. (C) Anti-c-Abl immunoprecipitates from the lysates of HEK and HEK/NOX5 cells were immunoblotted with antibodies to c-Abl and NOX5. (D) Immunoblots with antibodies to cAbl, NOX5, and PDI (loading control) were performed using crude membranes preparations from K562/NOX5 cells expressing GFP-c-Abl or GFP-KD-c-Abl and treated with or without H2O2.. E, F) After densitometric analysis, the levels of Abl proteins (GFP-Abl plus endogenous c-Abl proteins) and NOX5 proteins were normalized to the corresponding PDI protein levels and expressed as a percentage of the control value (100%) obtained from H2O2-untreated cells. Data are the mean +/− SEM of three independent experiments. (G) K562/NOX5 cells and K562/NOX5 cells expressing GFP-c-Abl or GFP-KD-c-Abl were treated with or without H2O2 (100 μM) for 10 minutes, then crude membranes were prepared and assayed for superoxide generation using SOD-inhibitable cytochrome c reduction. The data represent the H2O2-induced fold increase in superoxide formation and are the means +/− SEM of 3–7 independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistical significance versus the fold increase in NOX5 activity measured using K562/NOX5 cells. * P < 0.05 or ns. The inset in Fig. 8D is a representative cytochrome assay performed with membranes of untreated K562/NOX5 cells. The graph depicts the Δ 50nm absorbance as a function of time.