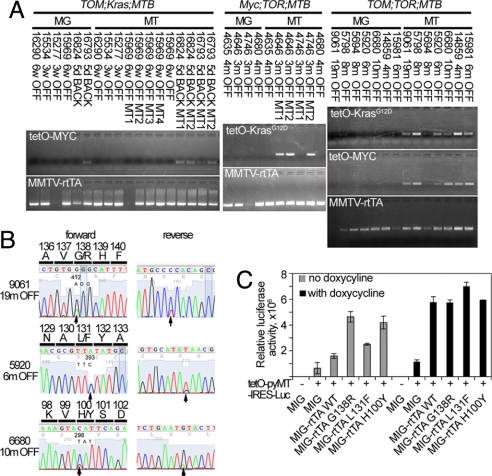
Fig. 4.
Loss of doxycycline dependence in tumors from TOM;TOR;MTB and Myc;TOR;MTB mice is associated with somatic mutations in the MMTV-rtTA transgene. (A) Analysis of transgene reactivation in recurrent tumors from TOM;Kras;MTB (Left), Myc;TOR;MTB (Center), and TOM;TOR;MTB (Right) animals. Paired RNA samples from recurrent tumor and non-tumor-bearing mammary gland were collected after removal OFF doxycycline or after placing the animals BACK on doxycycline as indicated and assayed as described in Experimental Procedures. (B) Examples of forward and reverse sequencing traces from tumor samples: 9061, 19 m OFF; 5920, 6 m OFF; 6680 10 m OFF by direct sequencing of rtTA amplification products with nucleotide and predicted amino acid changes indicated in the forward sequencing panel. (C) Luciferase activity of the three mutant rtTA clones is increased compared with wild-type rtTA and to mock-transfected controls with and without doxycycline addition. Wild-type and mutant rtTA was cloned into a modified MigR1 retroviral vector (33) and cotransfected into 293T cells with luciferase reporter pTetO-PyMT-IRES-Luc [Nancy Y.-C. Du (Memorial Sloan–Kettering Cancer Center) and H.E.V., unpublished work]. At 16 h after transfection, doxycycline was added to appropriate samples, and, 24 h later, cells were harvested, and luciferase activity for each sample was compared with the mock-transfected control to calculate the increase in luciferase activity.