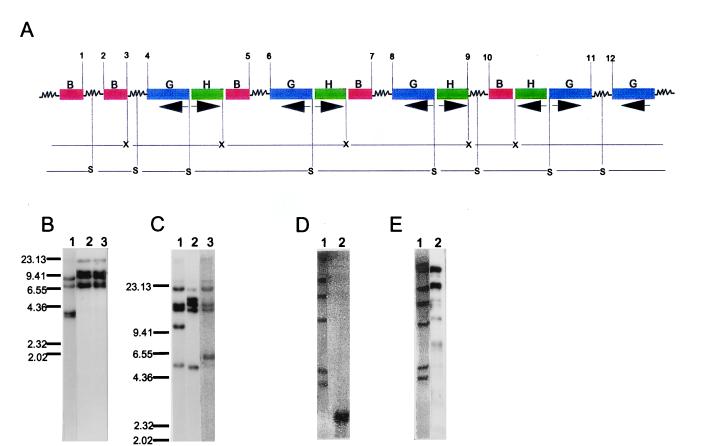
Figure 5.
(A) Molecular organization of the transgenes at a single locus in line K496-4. This represents one of the most complex cases. The locus has three units of the cointegrate plasmid integrated in tandem and one in an inverted configuration; in addition one gusA and twobar genes are present. Arrows under gusA and hpt indicate direction of transcription and therefore the direction in which the reverse primers for the two genes extend over the template in PCR. Numbers 1–12 delimit the regions of intervening sequences. X, XbaI; S, SacI; B, bar; G, gusA; H, hpt. (B) and (C) Southern hybridization results for K496-4 DNA digested with XbaI and SacI, respectively. Lanes 1–3, genomic DNA probed with coding regions of bar, gusA, and hpt, respectively. (D) Double digestion ofgenomic DNA of K496-4 with XbaI and SacI. All four copies of the hpt comigrate at the expected size of 1.2 kb. Lane 1, DNA size marker λ phage DNA digested with HindIII. Lane 2, genomic DNA probed with hpt coding region. (E) Southern hybridization of long PCR products obtained with reverse primers for hpt and gusA. Lane 1, DNA size marker λ phage DNA digested with HindIII. Lane 2, long PCR products probed with gusA coding region. The two dark bands represent two bands each. Numbers indicated on the side of B and C represent size marker in kb. These numbers apply for the size marker shown in lane 1 of D and E also.