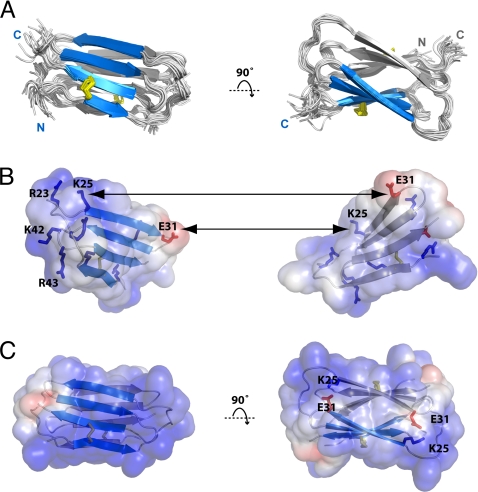
Fig. 2.
Structure of the Ltn40 dimer. (A) Ensemble of 20 NMR structures with backbone rmsd ≈0.5 Å. Disordered N- and C-terminal residues (residues 1–7 and 53–93) are not shown. (B) Hydrophobic and electrostatic stabilization of the Ltn40 dimer. Lys25 and a cluster of basic residues (blue) at one end of the dimer interface pair with Glu31 and other acidic side chains (red) at the other end of the opposing monomer. Aliphatic and aromatic residues in the center (white surface) form the hydrophobic core of the dimer. (C) The electrostatic potential surface of the Ltn40 dimer is highly positive, owing to the large number of basic residues.