Figure 7.
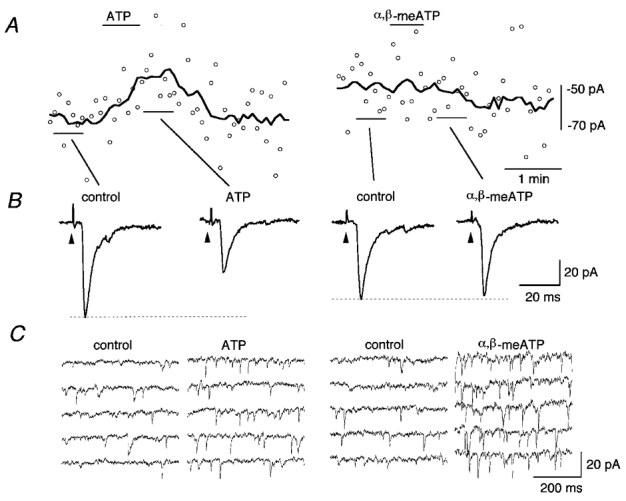
Effects of ATP and α,β-methylene ATP (α,βmeATP) on the eEPSCs and sEPSCs of a cNTS neurone
A, eEPSC amplitude (○) and the moving average over nine consecutive stimuli (thick line). Left, effect of ATP (10−4 m); right, effect of α,βmeATP (10−4 m). The drugs were applied at the horizontal bars above the traces. B, averaged waveform of eEPSC. Stimulus-triggered average of four consecutive eEPSCs. The solitary tract was stimulated at the arrowheads every 5.01 s. From left to right, before ATP, during ATP, before α,βmeATP, and during α,βmeATP. C, consecutive fast-sweep traces showing the effect of ATP and α,βmeATP on the occurrence of sEPSCs. All traces in C were selected from the periods in which there was no stimulation. A-C were from a recording in the same cNTS neurone.
