Figure 11.
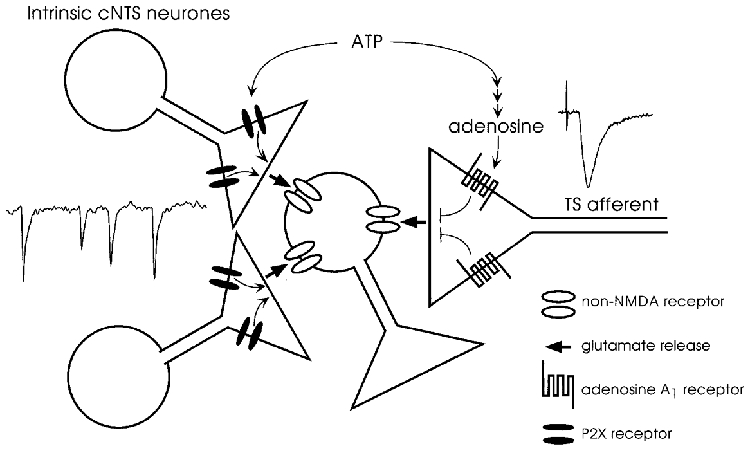
Schema for the interpretation of the opposite effects of ATP on the evoked and spontaneous excitatory inputs converging on a single second-order cNTS neurone
ATP activates directly the P2X receptors located at the presynaptic terminal of the intrinsic cNTS neurones to facilitate glutamate release. Adenosine, produced from ATP by a chain of ecto-enzymes, activates presynaptic A1 receptors located at the terminal of solitary tract afferents to suppress action potential-dependent release of glutamate (see text for detail).
