Figure 2. Effect of three weak bases on pHi and [Ca2+]i of snail neurones.
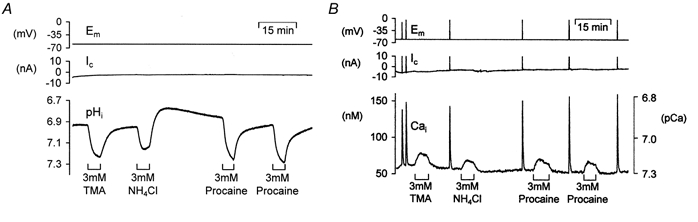
A, the snail neurone was voltage clamped at -60 mV and pressure injected with HPTS (approximate final intracellular concentration 200 μm). Intracellular alkalinizations were induced by superfusing with 3 mm trimethylamine (TMA), 3 mm ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and 3 mm procaine for ∼5 min. B, another snail neurone was held at -60 mV and pressure injected with fura-2 (approximate final concentration 50 μm). Superfusion with 3 mm trimethylamine (TMA), 3 mm ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and 3 mm procaine for ∼5 min all resulted in a transient rise in [Ca2+]i. The neurone was periodically depolarized (burst of 10 steps to 0 mV for 100 ms at 5 Hz) to maintain store calcium levels.
