Figure 5. Effects of 20 mm Pi in the presence and absence of CP.
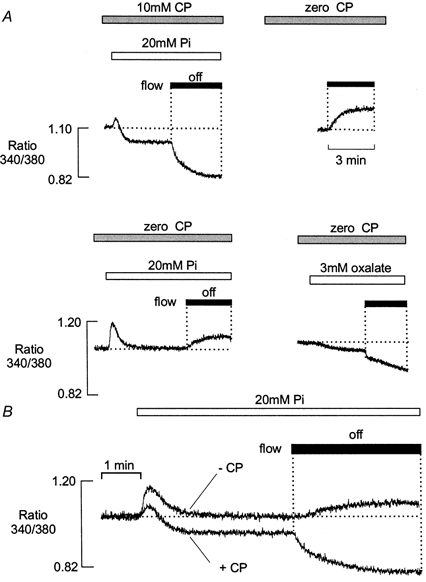
A, after 10 min equilibration in a solution containing 10 mm CP, introduction of 20 mm Pi caused a small transient rise in [Ca2+] and a maintained decrease in resting [Ca2+]. A further reduction in bathing [Ca2+] occurred when the flow was stopped (left). Following equilibration with a solution lacking CP, [Ca2+] increased when the flow was stopped (right). In the absence of CP, introduction of 20 mm Pi induced a larger transient increase in [Ca2+], which then declined to the control level. A maintained increase in [Ca2+] occurred when the flow was subsequently stopped (lower left). Introduction of 3 mm oxalate resulted in a maintained decrease in the resting [Ca2+], which became more pronounced when the flow was stopped (lower right). B, superimposed fluorescence records showing changes in [Ca2+] on exposure to 20 mm Pi in the presence and absence of 10 mm CP. All responses were obtained from the same preparation. In this example, the free [Ca2+] was increased to 250 nm to increase the possibility of Ca-Pi precipitation. All results were obtained from the same preparation.
