Figure 3. Effects of PO2 upon ISC, GNa and the Na+ extrusion capacity of the Na+ pump.
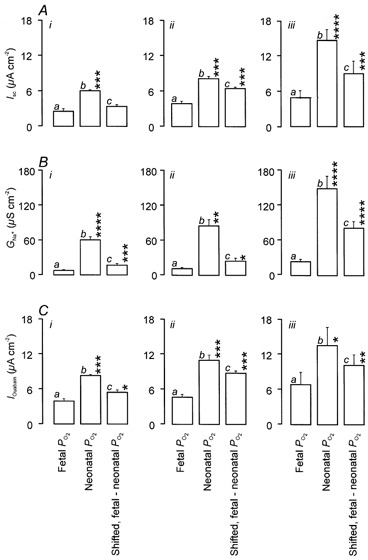
Experiments were undertaken using cultured epithelia maintained continually at either fetal (a) or neonatal alveolar PO2 (b), or exposed to a shift in PO2 equivalent to that seen at birth (c). This manoeuvre was undertaken 6 h (ic), 24 h (iic) or 48 h (iiic) before the cells were used in experiments (n = 5 for each). The cells used had been cultured for a total of 48 h (i and ii) or 72 h (iii). A, the total ISC recorded from cells maintained under the 3 culture regimes. B, estimates of GNa derived from experiments undertaken using basolaterally permeabilised cells. C, the capacity of the basolateral Na+ pump estimated from the ouabain-evoked fall in ISC measured in apically permeabilised cells. Asterisks denote values that differed significantly (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.02, ***P < 0.01, ****P < 0.001) from the appropriate control data derived from cells that had been maintained continually at fetal PO2 (ia, iia and iiia).
