Figure 5. Plasma osmolality after hypertonic loads.
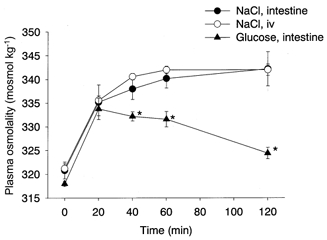
Intestinal infusion of 10 ml kg−1 of 3.6 % NaCl (•, n = 5) for 10 min and intravenous infusion of the same amount of NaCl (3.3 ml kg−1 of 10.8 % solution, ○, n = 5) for 30 min elevated the plasma osmolality with a similar time course and magnitude. Intestinal infusion of 10 ml kg−1 20 % glucose (▴, n = 5) for 10 min increased the plasma osmolality to a peak at 20 min, which then slowly returned to the baseline level. Stars show significant difference between groups.
