Figure 7. Effect of depolarization-induced Ca2+ influx on NMDA- and AMPA-mediated components of EPSCs.
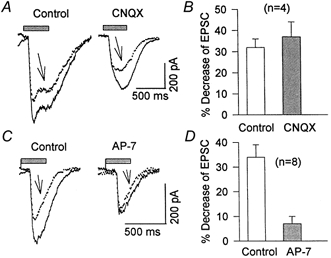
A, light-evoked EPSCs were recorded before (Control), and after (arrows) a depolarizing voltage step from -70 to 0 mV (not illustrated) in the absence (Control) and the presence of 2 μm CNQX. B, histogram summarizing the depolarization-induced inhibition of EPSCs in the absence (32 ± 2 %) and presence of 2-5 μm CNQX (37 ± 7 %). C, AMPA receptor-mediated EPSC recorded in drug-free Mg2+-free Ringer solution (left) or in the presence of 50 μm AP-7. A depolarizing step of 400 ms from -70 to 0 mV (as in A; traces indicated by arrows), reduced light-evoked EPSCs by only 7 ± 3 %, which was significantly (P < 0.05) smaller than the 34 ± 5 % inhibition seen in the absence of AP-7 (Control). D, histogram summarizing these data.
