Figure 1. Suppressive effect of 5-HT on the EPSC evoked in ventral horn neurons by stimulation of reticulospinal axons.
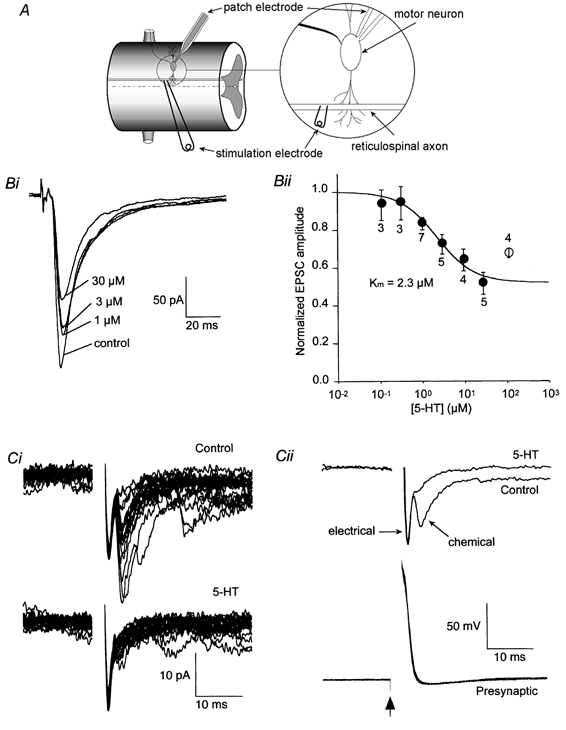
A, schematic diagram of recording configuration. Postsynaptic neurons were recorded under whole-cell voltage clamp. Presynaptic axons were stimulated either extracellularly as in B or via an intracellular recording microelectrode as in C. Bi, EPSCs recorded in control solution and with increasing doses of superfused 5-HT (1, 3 and 30 μm). The holding potential was -70 mV. Bii, mean dose-response data (±s.e.m.) obtained as in Bi. Numbers by each symbol indicate the number of cells. The continuous line is the best-fit through the points (0.1-30 μm) with the form 1 - {Fmax[5-HT]/([5-HT]+Km)}, where Fmax is the maximum fractional suppression (0.49). Ci, postsynaptic responses to action potentials evoked in a synaptically paired presynaptic giant axon. The upper record is of 20 consecutive responses in control conditions, the lower traces in the presence of 30 μm 5-HT. Note that the application of 5-HT almost completely abolished the later variable chemical component but left the early electrical component unchanged. Cii: top, the mean postsynaptic response to presynaptic action potentials (bottom) before and after application of 5-HT. Means are taken from the data in Bi. Bottom: traces showing the presynaptic action potential evoked by a 2 ms depolarizing current pulse given at the time marked by the arrow in control and in the presence of 5-HT.
