Figure 3. Confocal micrographs of whole mount preparations of guinea-pig proximal colon and gastric fundus, showing double labelling of Kv1.1-LI (Alexa 488, green) and c-Kit-LI (Alexa 594, red) within the muscularis externa.
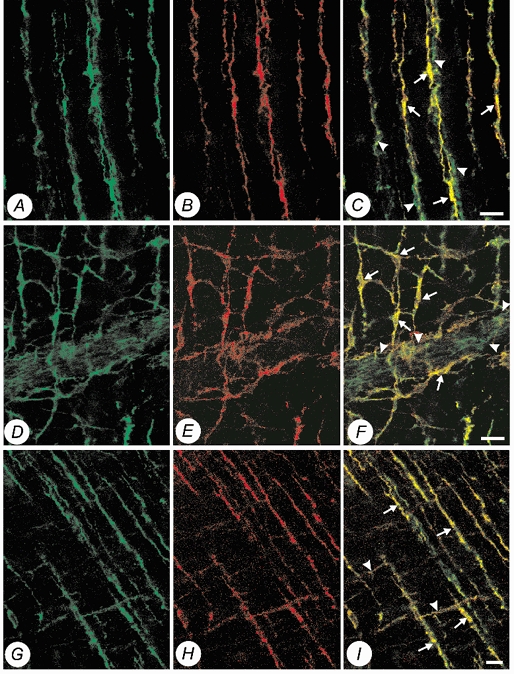
A, Kv1.1-LI (Alexa 488, green) within the circular muscularis of the proximal colon. B, c-Kit-LI (Alexa 594, red) within the circular muscularis of the same specimen. C, co-localization of Kv1.1-LI and c-Kit-LI (yellow) showing that intramuscular ICC (arrows) and juxtaposed varicose nerve fibres (arrowheads) express Kv1.1. D, Kv1.1-LI (Alexa 488, green) at the level of the myenteric plexus. E, c-Kit-LI (Alexa 594, red) at the level of the myenteric plexus in the same specimen. F, co-localization of Kv1.1-LI and c-Kit-LI (yellow) showing that both the cell bodies (arrows) and intricate processes of myenteric ICC are immunopositive for Kv1.1. Note also myenteric ganglia (arrowheads) are also immunopositive for Kv1.1. G, Kv1.1-LI (Alexa 488, green) within the circular and longitudinal muscularis of the gastric fundus. H, c-Kit-LI (Alexa 594, red) within the circular and longitudinal muscularis of the gastric fundus of the same specimen. I, co-localization of Kv1.1-LI and c-Kit-LI (yellow), showing that intramuscular ICC in both the longitudinal muscularis (arrowheads) and circular muscularis (arrows) are immunopositive for Kv1.1. (Scale bars, 20 μm.)
