Figure 5. Effect of high K+ concentration on deactivation kinetics of WT, HERGCΔ236 and HERGCΔ278 channels.
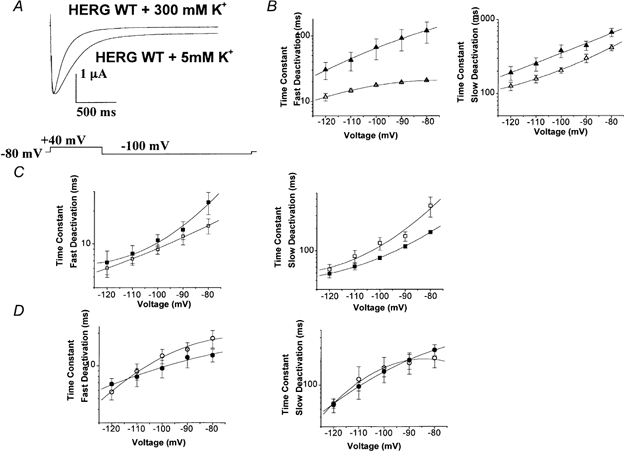
Deactivation kinetics were studied as in Fig. 3. A, high K+ accelerated the deactivation of WT channels. In this set of traces cells were held at −80 mV depolarized to +40 mV for 1 s and subsequently hyperpolarized to −100 mV for 3 s. B, fast and slow deactivation plots for WT HERG + 5 mm K+ (▴) and WT HERG + 300 mm K+ (▵), indicating that high K+ accelerated deactivation of WT HERG (n = 13, P = 0.011 for fast deactivation and P = 0.17 for slow deactivation). C, fast and slow deactivation plots for HERGCΔ236 + 300 mm K+ (□) and HERGCΔ236 + 5 mm K+ (□), indicating that high K+ did not alter the deactivation (n = 1, P = 0.41 for fast deactivation and P = 0.88 for slow deactivation). D, fast and slow deactivation plots for HERGCΔ278 + 300 mm K+ (^) and HERGCΔ278 + 5 mm K+ (•), indicating that high K+ did not alter deactivation (n = 11, P = 0.42 for fast deactivation and P = 0.33 for slow deactivation).
