Figure 5. Connectivity among inspiratory neurones and an expiratory motoneurone, and discharge patterns during fictive cough.
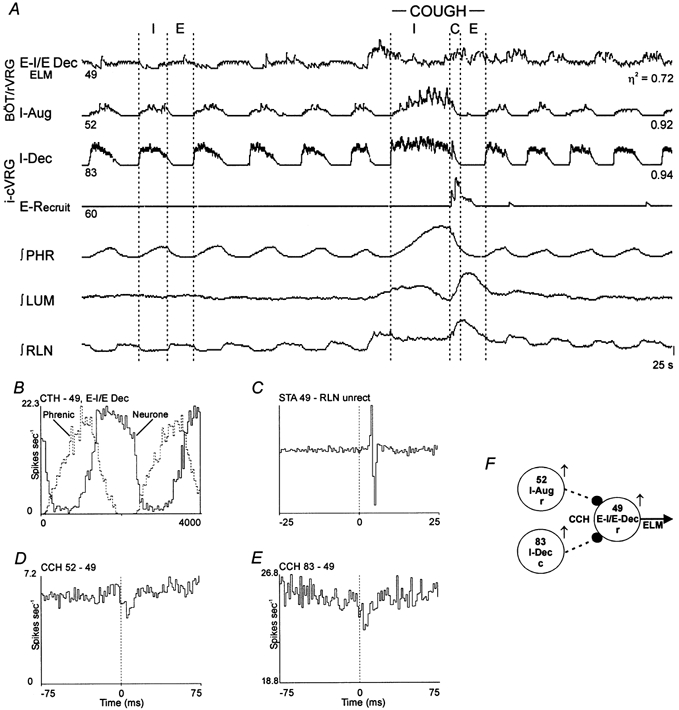
A, discharge patterns of two inspiratory and two expiratory neurones. Results suggest I-Aug neurone 52 and I-Dec neurone 83 inhibit expiratory motoneurone 49. B, CTH; 100 cycles averaged. C, STA; offset biphasic feature with a lag of 3.0 ms; number of trigger events, 39081. D, CCH; offset trough with a lag of 6.0 ms; half-width, 3.0 ms; detectability index, 5.2; correlation strength, 0.27; 39098 reference and 38274 target spikes. E, CCH; offset trough with a lag of 6.0 ms; half-width 4.5 ms; detectability index, 3.7; correlation strength, 0.14; 18590 reference and 63998 target spikes. Correlogram was scaled-up to show significant primary trough by subtraction of 70 % of the counts in the minimum bin from each bin. F, summary circuit of inferred connectivity.
