Figure 1. Polygraph record of a single trial during normoxic (A) and hypoxic (B) breathing.
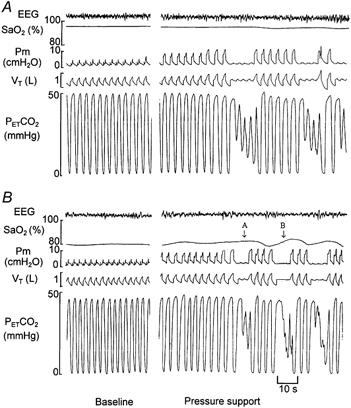
The baseline period shows spontaneous, stable breathing with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) of 2 cmH2O. During normoxia, the pressure-support level was increased to 8 cmH2O during inspiration with the end-expiratory level maintained at 2 cmH2O (8/2 cmH2O) and subsequently to 10/2 cmH2O. At 10/2 cmH2O, the reduction in PET,CO2 was sufficient to cause an initial hypopnoea and consequent periodic breathing. The hypopnoea threshold was determined as the mean PET,CO2 of the last three breaths immediately preceding the first hypopnoea. During hypoxia, arrow A indicates a hypopnoea with two successive untriggered breaths, and arrow B indicates a central apnoea with no respiratory effort.
