Figure 4. External Ca2+ and Mg2+ had similar effects on the surface potential.
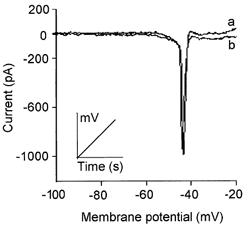
To study the effect of changes in [Ca2+]o on membrane current, avoiding the voltage shift due to the non-specific screening effect of Ca2+ ions, the solutions were balanced with Mg2+. This figure shows that the voltage at the peak of the Na+ current evoked by a voltage ramp (0.66 mV ms−1; inset) was not affected by changing the external solution from 4.5 mm Ca2+ and 0.5 mm Mg2+ (trace a) to 0.5 mm Ca2+ and 4.5 mm Mg2+ (trace b; Int 1 and Ext 13 in Table 1). The voltage at the peak was -43 ± 0.5 and -45 ± 3.4 mV with 4.5 mm Ca2+ and 4.5 mm Mg2+, respectively (n = 15). The difference was not significant (P > 0.05). This indicates that Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions exert the same screening effect on the negative fixed charges at the mouth of the Na+ channels.
