Figure 7. Effects of SNP (300 μm) on the electrical properties of the longitudinal smooth muscle.
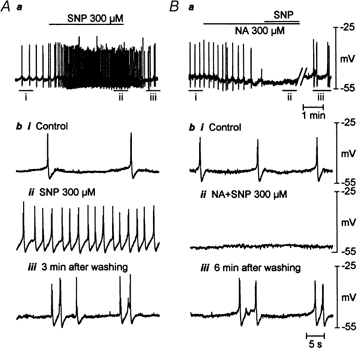
A and B, original intracellular micro-electrode recordings demonstrating effects of SNP in the absence and presence of niflumic acid (300 μm) from same cell. Ab and Bb, snapshots of original recordings from Aa and Ba on an expanded time scale. i, control. ii, drug application. iii, recovery after washout. SNP depolarized the resting membrane potential (RMP) and induced on-going spike-like action potentials (n = 6). Niflumic acid hyperpolarized RMP (n = 4), gradually decreased the amplitude of spike-like action potentials and finally abolished them. In the presence of niflumic acid, SNP failed to depolarize RMP and evoke on-going spike-like action potentials (n = 3).
