Table 1.
Effects of low-dose acetazolamide on respiratory parameters during hyperoxia
| Control | Acetazolamide | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| B (kPa) | 2.91 ± 0.57 | 0.78 ± 1.9 | 0.005 |
| SC (l min-1 kPa-1) | 0.45 ± 0.16 | 0.27 ± 0.13 | 0.001 |
| SP (l min-1 kPa-1) | 0.09 ± 0.07 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.123 |
| τP (s) | 5.91 ± 4.28 | 7.27 ± 5.76 | 0.741 |
| τon (s) | 83.60 ± 47.60 | 88.56 ± 25.28 | 0.756 |
| τoff (s) | 108.65 ± 45.04 | 128.98 ± 46.86 | 0.362 |
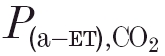 (kPa) (kPa) |
0.05 ± 0.57 | 0.43 ± 0.81 | 0.029 |
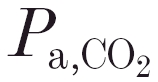 (kPa) (kPa) |
47.40 ± 3.62 | 46.95 ± 5.19 | 0.633 |
Parameter values obtained from the optimal fits in the analysis of DEF runs performed during hyperoxia (32 control runs and 27 runs after acetazolamide). B, the apnoeic threshold or X-intercept of the ventilatory CO2 response curve. SC and SP, the CO2 sensitivities of the central and peripheral chemoreflex loops, respectively. τp, time constant of the peripheral chemoreflex loops. τon and τoff, central time constants of responses to CO2 on-and off transients, respectively. 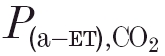 , arterial–end-tidal
, arterial–end-tidal 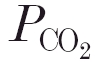 difference.
difference.
