Figure 2. Respiratory rhythm and synaptic drive amplitude after glibenclamide application.
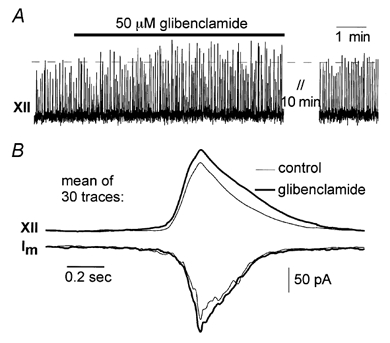
A, the amplitude of the integrated hypoglossal nerve (XII) activity increases after glibenclamide application. B, modulation of synaptic drives (membrane currents, Im, recorded in whole-cell mode at holding potential −60 mV) could only be discerned when 30 traces were averaged and smoothed. Synaptic drive amplitude increased with glibenclamide in parallel with hypoglossal activity.
