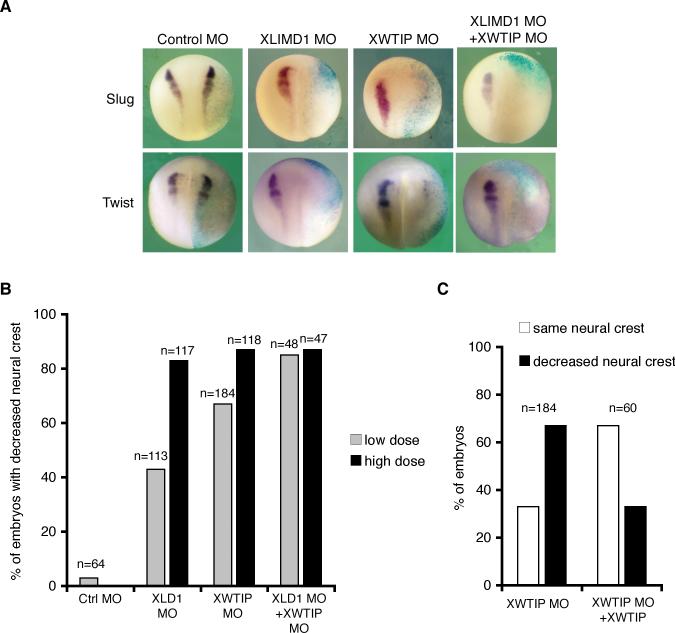
Figure 5. Depletion of XLIMD1 or XWTIP blocks neural crest development in Xenopus.
A. X. laevis embryos were co-injected with β-gal and control MO, XLIMD1 MO (20ng), XWTIP MO (10ng), or a combination of XLIMD1 and XWTIP MOs. Embryos were fixed at stage 18−19, and in situ hybridization for XSlug or XTwist performed. B. Graph displaying percent of embryos with decreased neural crest on injected side by Slug or Twist in situ hybridization following injection of low dose (gray columns; 10ng XLIMD1 MO, 5ng XWTIP MO) or high dose (black columns; 20ng XLIMD1 MO, 10ng XWTIP MO) of morpholinos. The total number of embryos injected is shown over each column (n). C. X. laevis embryos were co-injected with β-gal, the XWTIP MO (5ng) and XWTIP capped mRNA as shown. Black columns indicate the percent of embryos with decreased neural crest on the injected side (by Slug or Twist in situ) and white columns indicate the percent of embryos where neural crest was the same on the injected and uninjected sides. The total number of embryos injected is shown over each set of columns (n).