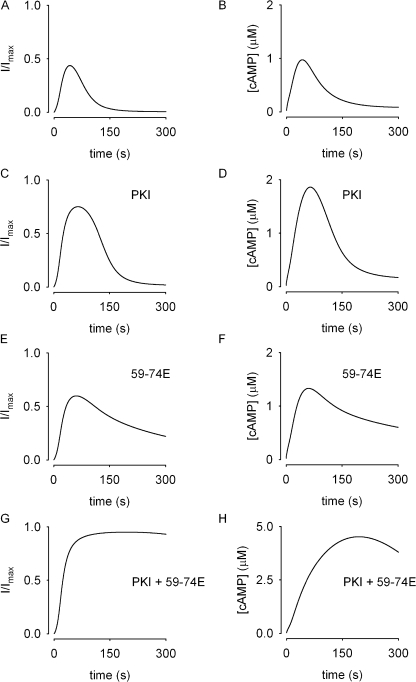
Figure 6.
Mathematical simulations of the system described by the schematic in Fig. 5. Panels on left depict the signal being measured, panels on right depict the underlying cAMP signals. (A and B) Simulations of normalized current through CNG channels (I/I max) due to isoproterenol-induced cAMP signals under control conditions. (C and D) Simulations of isoproterenol-induced currents and cAMP signals in the presence of 20 nM PKI (included in the pipette solution). Including PKI in the pipette solution inhibits PKA-mediated stimulation of PDE activity, allowing increased cAMP levels, but the signal is still transient due to basal PDE4 activity and GRK-mediated receptor desensitization. (E and F) Simulations describing the effect of GRK inhibition (3 μM 59-74E) on isoproterenol-induced signals. The signals are still transient due to PKA-mediated stimulation of PDE4 activity. (G and H) Simulations of currents and cAMP signals when both PKA and GRK activity are inhibited (with PKI and 59-74E). Inhibiting receptor desensitization and the stimulation of PDE4 activity prevents the decay of isoproterenol-induced signals.