Figure 5. Propagated glial Ca2+ waves evoke vasodilatation in distant arterioles.
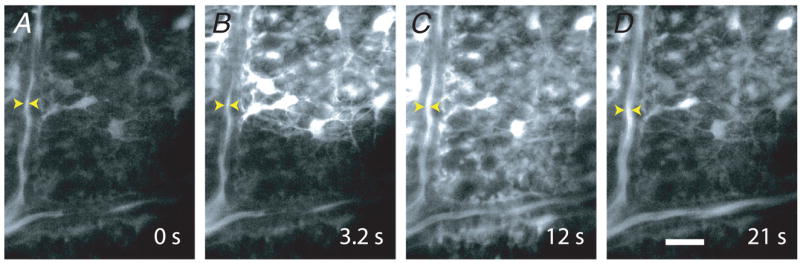
A–D, a Ca2+ wave produced by ejection of ATP propagates through glial cells at the surface of the retina. The Ca2+ wave dilates an arteriole when it reaches the vessel. The site of focal ATP ejection, used to initiate the Ca2+ wave, was just beyond the upper right corner of the images. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
