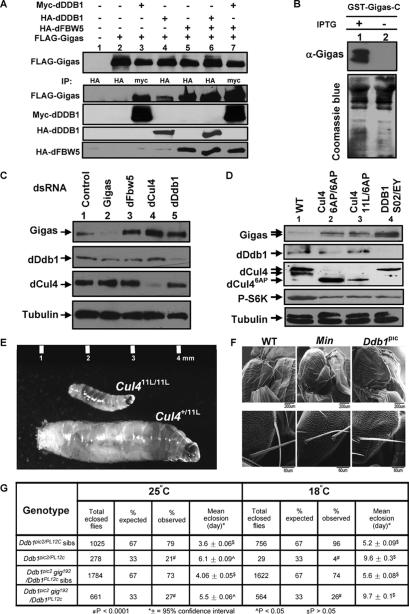
Figure 5.
Accumulation of Gigas/Tsc2 protein and growth defects in Drosophila Cul4 and Ddb1 mutants. (A) Drosophila S2 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing the indicated proteins, and protein–protein association was examined by coupled IP-Western analysis. (B) Characterization of an anti-Gigas antibody. Escherichia coli BL21 cells were transformed with a plasmid expressing a C-terminal portion of the Gigas protein, and were cultured in LB media with or without IPTG to induce the expression of GST-Gigas. Cells were lysed in SDS buffer followed by Western analysis. (C) S2 cells were treated with dsRNA targeting Gigas, dFbw5, dCul4, and dDdb1 and control dsRNA for 2 d. The cells were lysed in RIPA buffer followed by Western analysis with the indicated antibodies. (D) Gigas accumulates in Drosophila Cul4 and Ddb1 mutants. Total cell lysates were prepared from Drosophila Cul4 and Ddb1 mutant first instar larvae, and the steady-state levels of Cul4, Ddb1, Giags, tubulin, and phospho-S6K proteins were determined by direct Western blotting. (E) Size comparison of growth-arrested Cul411L/11L homozygous mutant larvae with a normal Cul411L/+ heterozygous sibling third instar larvae. (F) Drosophila hypomorphic Ddb1 mutants display small and missing macrochaete. Scanning electron micrographs of wild-type, Minute, and Ddb1pic2/PL12C mutant adults. (G) Growth defects of Cul4 and Ddb1 mutants are rescued by heterozygosity of gig (TSC2). Total eclosed flies and mean eclosion time of Ddb1pic2/Ddb1PL12c mutants and their siblings and Ddb1pic2gig192/Ddb1PL12c mutants and their siblings were measured at 18°C and 25°C.