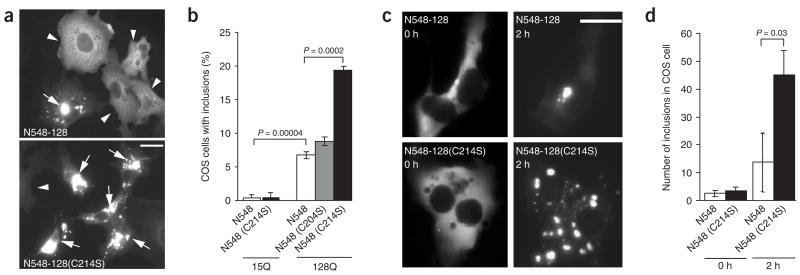
Figure 2.
Increased inclusions of palmitoylation-resistant mutant htt in COS cells. (a–d) COS cells were transfected with N548-128, with or without the C214S substitution, and stained with htt antibody. (a) Inclusion bodies (arrows) were occasionally seen with the expression of N548-128. However, a C214S substitution altered mutant htt distribution and increased the formation of inclusions. Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) The percentage of cells containing inclusions increased in COS cells expressing N548-128 (mean ± s.e.m.: 6.7 ± 0.46%) and was maximal in cells expressing N548-128(C214S) (19.4 ±± 0.58%). This effect was not observed with N548-128(C204S) (8 ± 0.68%). (c) Time-lapse images captured over 2 h revealed that inclusions developed at an accelerated rate in the presence of the C214S substitution in mutant htt (bottom). Scale bar, 10 μm. (d) The rate of inclusion formation in cells transfected with N548-128(C214S) was significantly (P = 0.03) faster than in cells transfected with N548-128.